TransStart® FastPfu Fly DNA Polymerase
FastPfu Fly 快速高保真DNA 聚合酶
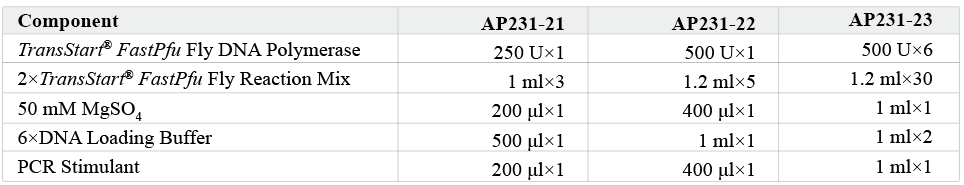
目录号: AP231-21
单 价:¥770
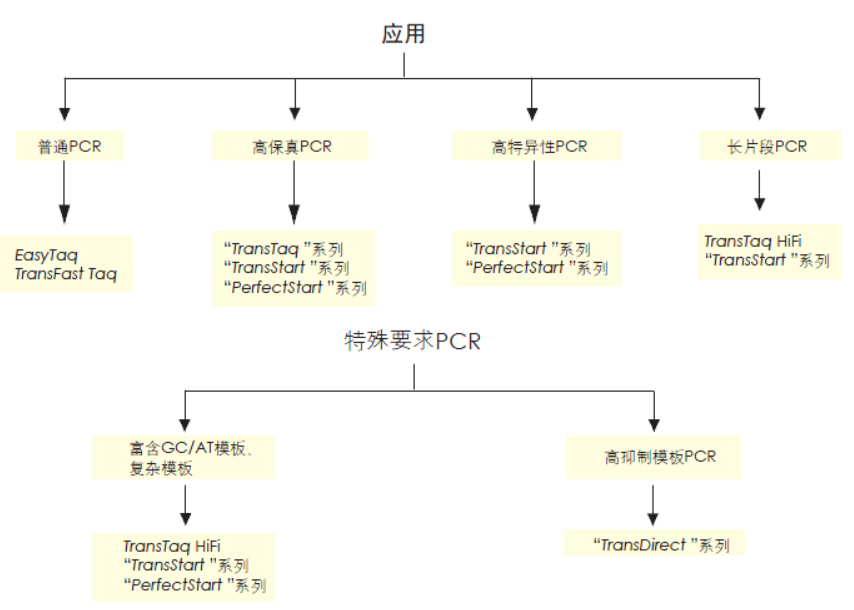
产品详情介绍
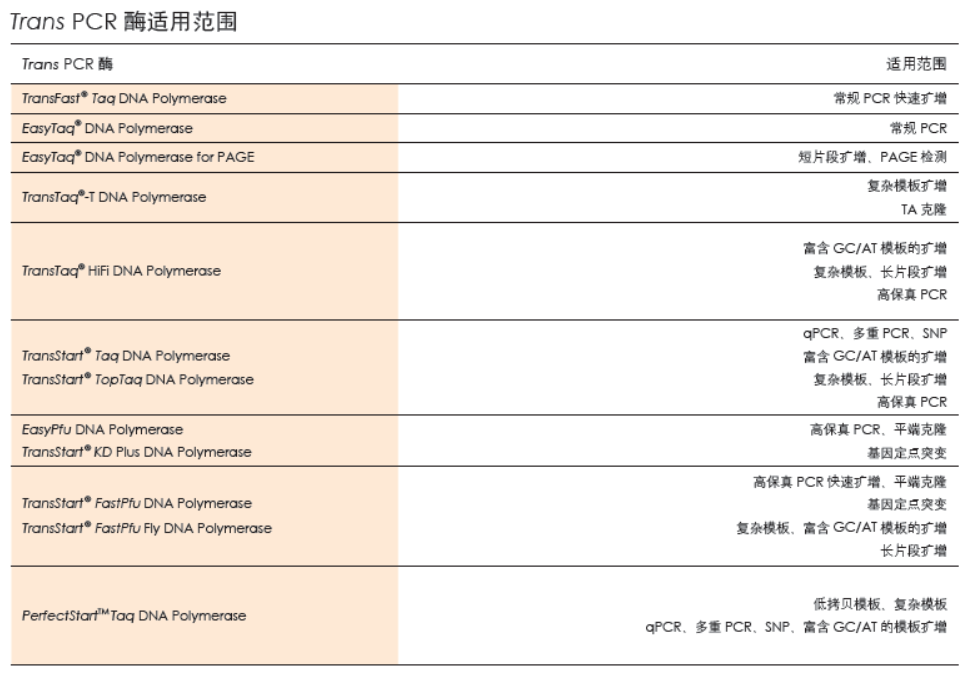
TransStart®FastPfu Fly DNA Polymerase是用于快速PCR的热启动超高保真DNA聚合酶。该酶与TransStart® FastPfu DNA Polymerase相比,扩增速度更快(≤5 kb基因可实现12 kb/min的极速扩增,>5 kb基因可达到6 kb/min高速扩增),扩增效率更高,产量更高,保真性更高,灵敏度更高。2×TransStart® FastPfu Fly Reaction Mix中已含有dNTPs,DNA扩增时,只需加入模板、引物、水和TransStart® FastPfu Fly DNA Polymerase,使Reaction Mix的浓度为1×即可进行反应。扩增产物为平末端,可直接克隆于pEASY®-Blunt系列载体中。
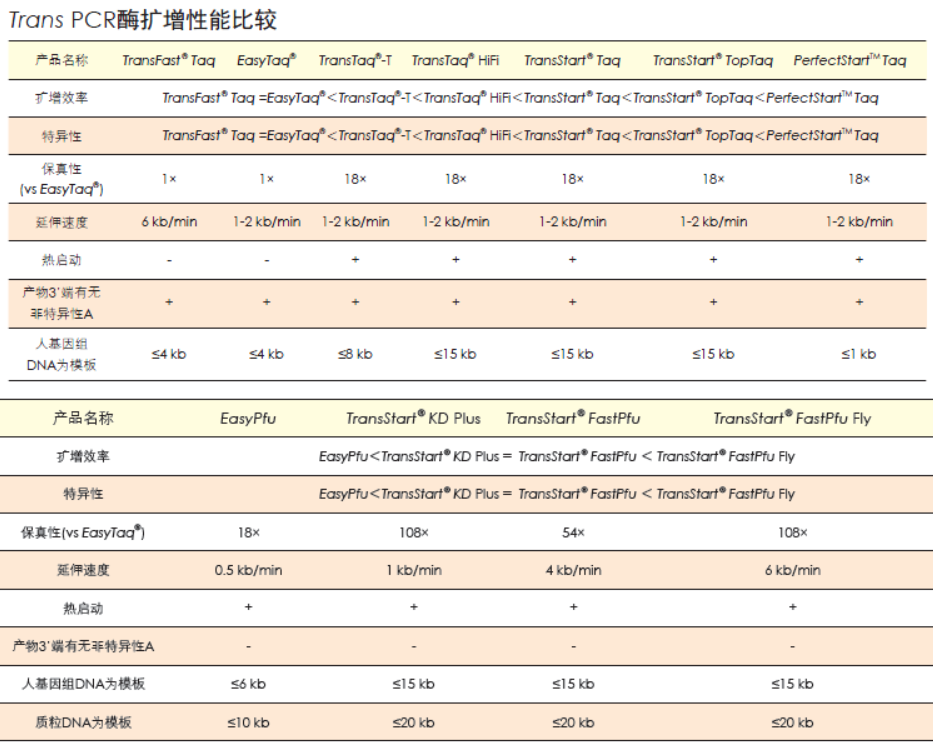
• 保真性是EasyTaq® DNA Polymerase的108倍。
• 扩增产物为平末端,可直接克隆于pEASY®-Blunt系列载体中。
• 基因组DNA片段的扩增(≤15 kb)。
• Plasmid DNA片段扩增(≤ 20 kb)。

使用TransGen、Company TA及Company N产品,分别以人gDNA为模板,进行不同基因的PCR扩增,1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析扩增效果。

1.Xu Y, Zhu T F. Mirror-image T7 transcription of chirally inverted ribosomal and functional RNAs[J]. Science, 2022.(IF 63.71)
2.Niu X, Tang W, Liu Y, et al. Prime editor-based high-throughput screening reveals functional synonymous mutations in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2025.(IF 41.70)
3.Niu L, Shen W, Shi Z, et al. Three-dimensional folding dynamics of the Xenopus tropicalis genome[J]. Nature Genetics, 2021.(IF 38.33)
4.Duan Z, Liang Y, Sun J, et al. An engineered Cas12i nuclease that is an efficient genome editing tool in animals and plants[J]. The Innovation, 2024.(IF 33.20)
5.Huang M E, Qin Y, Shang Y, et al. C-to-G editing generates double-strand breaks causing deletion, transversion and translocation[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2024.(IF 21.30)
6.Wang D, Yan F, Wu P, et al. Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway[J]. Nature Communications, 2022.(IF 17.69)
7.Jin S, Fei H, Zhu Z, et al. Rationally designed APOBEC3B cytosine base editors with improved specificity[J]. Molecular cell, 2020.(IF 15.58)
8.Zhang A, Shan T, Sun Y, et al. Directed evolution rice genes with randomly multiplexed sgRNAs assembly of base editors[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023.(IF 13.80)
9.Zhang Y F, Yun J H, Zhang G Y, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from glucose through multidimensional engineering of Escherichia coli[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023.(IF 11.40)
10.Wang J L, Wang M, Zhang L, et al. WAV E3 ubiquitin ligases mediate degradation of IAA32/34 in the TMK1-mediated auxin signaling pathway during apical hook development[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2024.(IF 11.10)
11.Wang Y, Li S Y, Wang Y Z, et al. ZmASY1 interacts with ZmPRD3 and is crucial for meiotic double‐strand break formation in maize[J]. New Phytologist, 2023.(IF 9.40)
12.Li J, Bai Y, Liu Y, et al. Transcriptome-based chemical screens identify CDK8 as a common barrier in multiple cell reprogramming systems[J]. Cell Reports, 2023.(IF 8.80)
13.Jiang L, Yao B, Zhang X, et al. Salicylic acid inhibits rice endocytic protein trafficking mediated by OsPIN3t and clathrin to affect root growth[J]. The Plant Journal, 2023.(IF 7.20)
14.Tan Y, Yan X, Sun J, et al. Genome‐wide enhancer identification by massively parallel reporter assay in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Journal, 2023.(IF 7.20)
15.Chen J, Hu X, Shi T, et al. Metabolite‐based genome‐wide association study enables dissection of the flavonoid decoration pathway of wheat kernels[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020.(IF 6.84)
16.Zhu J, Miao Q, Tang J, et al. Nucleolin mediates the internalization of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus through clathrin-dependent endocytosis[J]. PLoS pathogens, 2018.(IF 6.16)
17.Chen J, Wang H, Yang X, et al. Consumption of miRNA-mediated insect-resistant transgenic rice pollen does not harm Apis mellifera adults[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021.(IF 5.30)