文章信息
文章题目:FOCAS: Transcriptome-wide screening of individual m6A sites functionally dissects epitranscriptomic control of gene expression in cancer
期刊:Cell
发表时间:2025 年 12 月 31 日
主要内容:北京大学生命科学学院、北大-清华生命科学联合中心、北京大学核糖核酸北京研究中心刘君课题组在 Cell 发表了题为“FOCAS: Transcriptome-wide screening of individual m6A sites functionally dissects epitranscriptomic control of gene expression in cancer”的研究论文。该研究建立了 FOCAS(Functional m6A Sites Detection by CRISPR-dCas13b-FTO Screening)方法,实现了 m6A 功能研究在位点分辨率上的关键突破。FOCAS 基于改造的 CRISPR-dCas13b 系统,将去甲基化酶 FTO 精准定位至 RNA 特定区域,从而在不改变 DNA/RNA 序列和不显著影响全局 m6A 水平的前提下,实现对特定 m6A 修饰位点的靶向去甲基化。这一策略不仅适用于 mRNA,还可以同时覆盖非编码 RNA,为在全转录组尺度上系统解析 m6A 的功能提供了技术基础。
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.11.037
使用TransGen产品:
6×Protein Loading Buffer(DL101)
Trans5α Chemically Competent Cell (CD201)
TransDB3.1 Chemically Competent Cell (CD531)

背景介绍
N6-甲基腺苷(m6A)作为真核生物 mRNA 中最普遍且功能最为多样的修饰形式之一,已有大量研究表明其可通过调控 RNA 剪接、稳定性、翻译及降解过程,深度参与基因表达调控。此外,m6A 修饰同样存在于包括染色质相关调控 RNA(carRNAs)在内的多种非编码 RNA 中,参与染色质功能调控。现有研究策略多基于对 m6A 调节因子的全局性干预,这种方法难以区分不同 RNA 分子、不同修饰位点在不同细胞环境下的功能差异,从而限制了对 m6A 精细调控逻辑的深入解析。
文章概述
基于 FOCAS 策略,研究团队在四种人类癌细胞系中系统分析了 m6A 修饰对细胞增殖的影响,并鉴定出 4475 个相关功能基因。这些基因大多此前未明确与 m6A 或肿瘤相关,表明 m6A 在癌细胞中的调控范围超出当前认知。进一步分析显示,m6A 调控具有高度异质性和基因背景依赖性:同一基因内不同 m6A 位点可通过不同机制影响 RNA 命运,甚至产生相反表型效应,这主要源于不同阅读蛋白的选择性结合。FOCAS 策略系统揭示了这种依赖于位点、阅读蛋白及细胞环境的精细调控模式。
应用 FOCAS 进一步探究 carRNA 上 m6A 修饰的功能,发现在增强子 RNA(eRNAs)、启动子相关 RNA(paRNAs)及转座子来源 RNA(reRNAs)三类 carRNA 中,均存在影响肿瘤增殖的关键 m6A 位点,提示 carRNA 上的 m6A 修饰具有重要调控作用。分析显示,同一基因背景下,mRNA 与其邻近 carRNA 区域难以同时筛选出有效 sgRNA;且大部分携带关键 m6A 位点的 carRNA,其邻近编码基因与肿瘤特征相关性较低,表明 m6A 修饰的 carRNA 更倾向于通过反式调控机制发挥作用。
通过比较四种细胞系中关键 m6A 峰 (FiPeaks),将其划分为广泛型(Universal-FiPeaks)和特异型(Unique-FiPeaks)。结果表明,尽管多数 m6A 峰在四种细胞系中普遍存在,但其调控细胞生长的作用通常具有细胞特异性,说明关键 m6A 位点的功能取决于其特定的生物学特性,而非修饰本身的存在与否。进一步分析发现,Universal-FiPeaks 主要富集于 mRNA,相关基因在多种肿瘤中功能一致且与患者预后相关;Unique-FiPeaks 则更多富集于 carRNA,提示非编码 RNA 上的 m6A 修饰在肿瘤类型特异性调控中起关键作用。该功能分层为 RNA 修饰的精准靶向和肿瘤特异性干预提供了理论依据。
FOCAS 分析还揭示了 m6A 修饰与转录调控网络的耦合关系。在肝癌细胞中,研究鉴定出一组受 m6A 调控、呈现“模块化”协同表达的关键转录调节因子。其中,KCTD1 被鉴定为一个此前未被报道的、受 m6A 调控的潜在泛癌抑癌因子,并能调控 H3K4me3 组蛋白修饰水平。这一发现凸显了 FOCAS 在揭示关键功能基因及其作用机制方面的优势。
综上所述,该研究利用 FOCAS 实现了对关键 m6A 修饰位点的精细功能解析,揭示特定 m6A 位点可作为独立的调控单元,直接参与基因表达和细胞命运的决定。FOCAS 不仅为阐释 m6A 的复杂调控机制提供了方法论支持,也为发展基于 RNA 修饰的肿瘤精准治疗奠定了基础。
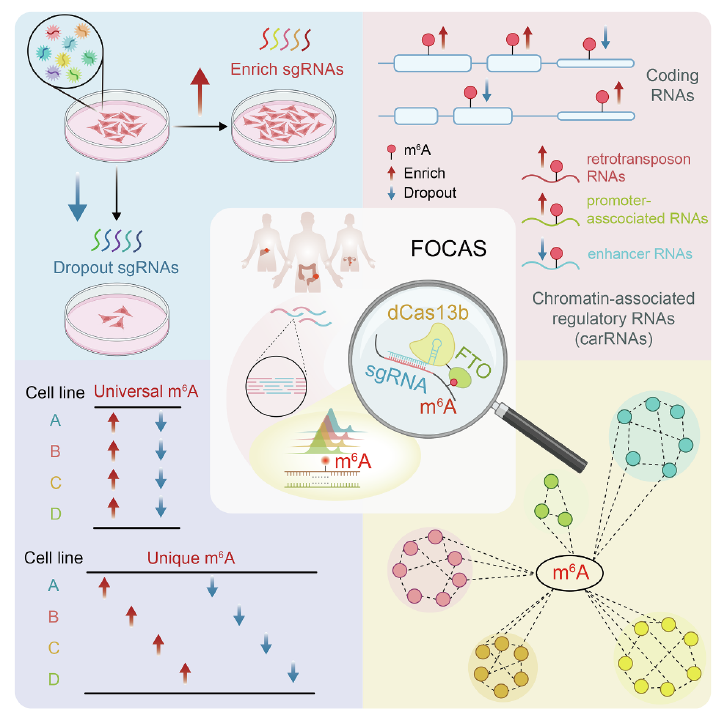
FOCAS 方法鉴定肿瘤中全转录组关键 m6A 位点并解析其调控模式
全式金生物产品支撑
优质的试剂是科学研究的利器。全式金生物的蛋白电泳缓冲液(DL101)、Trans5α 克隆感受态细胞(CD201)、TransDB3.1 克隆感受态细胞(CD531)助力本研究。产品自上市以来,深受客户青睐,多次荣登知名期刊,助力科学研究。
6×Protein Loading Buffer(DL101)
本产品是蛋白质样品进行 SDS 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳 (SDS-PAGE) 用 Loading Buffer。将其加入蛋白样品中,使其工作浓度为 1×,即可上样电泳。
产品特点
• 抑制降解,蛋白变性后更稳定。
• 采用新型还原剂,可高效还原二硫键。
• 加样不漂样,避免样品污染。
Trans5α Chemically Competent Cell (CD201)
本产品经特殊工艺制作,可用于 DNA 的化学转化。使用 pUC19 质粒 DNA 检测,转化效率高达 108 cfu/μg DNA 以上。
产品特点
• 适用于蓝白斑筛选。
• rec A1 和 end A1 的突变有利于克隆 DNA 的稳定和高纯度质粒 DNA 的提取。
TransDB3.1 Chemically Competent Cell (CD531)
本产品含有 gyrA462 基因,对 ccdB 基因产物的毒性具有抵抗作用。使用 pUC19 质粒 DNA 检测,转化效率高达 108 cfu/μg DNA 以上。
产品特点
• 适用于转化和扩增包含 ccdB 基因的质粒载体。
• 带有硫酸链霉素抗性。
全式金生物的产品再度亮相 Cell 期刊,不仅是对全式金生物产品卓越品质与雄厚实力的有力见证,更是生动展现了全式金生物长期秉持的“品质高于一切,精品服务客户”核心理念。一直以来,全式金生物凭借对品质的执着追求和对创新的不懈探索,其产品已成为众多科研工作者信赖的得力助手。展望未来,我们将持续推出更多优质产品,期望携手更多科研领域的杰出人才,共同攀登科学高峰,书写科研创新的辉煌篇章。
使用6×Protein Loading Buffer(DL101)产品发表的部分文章:
• Lan F, Li J, Miao W, et al. GZMK-expressing CD8+ T cells promote recurrent airway inflammatory diseases[J]. Nature, 2025.(IF 48.50)
• Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. FOCAS: Transcriptome-wide screening of individual m6A sites functionally dissects epitranscriptomic control of gene expression in cancer[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Zang X, He X Y, Xiao C M, et al. Circular RNA-encoded oncogenic PIAS1 variant blocks immunogenic ferroptosis by modulating the balance between SUMOylation and phosphorylation of STAT1[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2024. (IF 27.70)
• Jin X, Xia T, Luo S, et al. Exosomal lipid PI4P regulates small extracellular vesicle secretion by modulating intraluminal vesicle formation[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2023. (IF 15.50)
• Zhai X, Kong N, Zhang Y, et al. N protein of PEDV plays chess game with host proteins by selective autophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2023. (IF 14.60)
• Gong H, Wang T, Wu M, et al. Maternal effects drive intestinal development beginning in the embryonic period on the basis of maternal immune and microbial transfer in chickens[J]. Microbiome, 2023. (IF 13.80)
• Zhang Q, Yang X, Wu J, et al. Reprogramming of palmitic acid induced by dephosphorylation of ACOX1 promotes β-catenin palmitoylation to drive colorectal cancer progression[J]. Cell discovery, 2023. (IF 13.00)
使用Trans5α Chemically Competent Cell (CD201) 产品发表的部分文章:
• Zhong S, Ding W, Sun L, et al. Decoding the development of the human hippocampus[J]. Nature, 2020.(IF 50.50)
• Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. FOCAS: Transcriptome-wide screening of individual m6A sites functionally dissects epitranscriptomic control of gene expression in cancer[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Wang J L, Sha X Y, Shao Y,et al. Elucidating pathway-selective biased CCKBR agonism for Alzheimer's disease treatment[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Kang X, Li X R, Zhou J Q, et al. Extrachromosomal DNA replication and maintenance couple with DNA damage pathway in tumors[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Jiang Y, Dai A R, Huang Y W, et al. Ligand-induced ubiquitination unleashes LAG3 immune checkpoint function by hindering membrane sequestration of signaling motifs[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Ou X M, Ma C Y, Sun D J, et al. SecY translocon chaperones protein folding during membrane protein insertion[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Zhao Y, Ping Y Q, Wang M W, et al. Identification, structure and agonist design of an androgen membrane receptor[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Wen X, Shang P, Chen H D, et al. Evolutionary study and structural basis of proton sensing by Mus GPR4 and Xenopus GPR4[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Hu Q L, Liu H H, He Y J, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of strigolactone perception in rice [J]. Cell, 2024.(IF 45.50)
• Shang P, Rong N, Jiang J J, et al. Structural and signaling mechanisms of TAAR1 enabled preferential agonist design[J]. Cell, 2023.(IF 45.50)
• Ma X J, Wang W, Zhang J Y, et al. NRT1.1B acts as an abscisic acid receptor in integrating compound environmental cues for plants[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 42.50)
• Jiang L, Xie X, Su N, et al. Large Stokes shift fluorescent RNAs for dual-emission fluorescence and bioluminescence imaging in live cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2023.(IF 36.10)
使用TransDB3.1 Chemically Competent Cell (CD531) 产品发表的部分文章:
• Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. FOCAS: Transcriptome-wide screening of individual m6A sites functionally dissects epitranscriptomic control of gene expression in cancer[J]. Cell, 2025.(IF 45.50)
• Medina-Puche L, Tan H, Dogra V, et al. A defense pathway linking plasma membrane and chloroplasts and co-opted by pathogens[J]. Cell, 2020.(IF 38.64)
• Zhang Y, Li X, Gao S, et al. Genetic reporter for live tracing fluid flow forces during cell fate segregation in mouse blastocyst development[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023.(IF 23.90)
• Guo J, Yu W, Li M, et al. A DddA ortholog-based and transactivator-assisted nuclear and mitochondrial cytosine base editors with expanded target compatibility[J]. Molecular Cell, 2023(IF 16.00)







